Introduction
The PATH environment variable in Linux tells the system which directories to search for executable files. By using the PATH variable, users can run commands without needing to specify their full paths.
This article will guide you on how to add a directory to the PATH, both temporarily and permanently, as well as how to remove a directory from the PATH in Linux.
Prerequisites
- Access to the terminal.
- A text editor.
What Is Linux PATH?
When a command is issued in the terminal, the system needs to find and execute the corresponding program. Hence, Linux relies on the PATH variable to designate directories containing programs and guide the system in locating the appropriate executable.
How to View the Directories in PATH
To print all the configured directories in the system’s PATH variable, run the echo command:
echo $PATH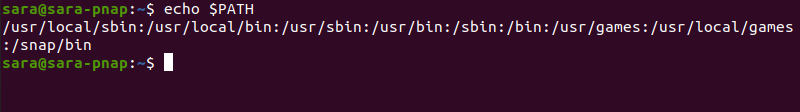
The output displays the directories configured in PATH by default. The same output can be obtained using the printenv command.
printenv PATH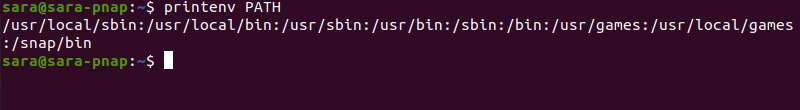
Moreover, running which on a specific command reveals the location of its executable. For example, execute which with whoami:
which whoami
The output indicates that the executable for whoami is located in the /usr/bin/ directory.
How Do I Add a Directory to PATH in Linux?
Specific directories are added to PATH by default. Users can add other directories to PATH either temporarily or permanently.
Linux: Add to PATH Temporarily
Temporarily adding a directory to PATH affects only the current terminal session. When users close the terminal, the directory is automatically removed from PATH.
To temporarily add a directory to PATH, use the export PATH command:
export PATH="/Directory1:$PATH"
The command appended Directory1 from the Home directory to PATH. You can verify the result using:
echo $PATH
The output indicates that the directory has been successfully added to the variable. However, this configuration only persists for the current session.
Linux: Add to PATH Permanently
To permanently add a directory to PATH, edit the .bashrc file located in the Home directory. Follow these steps:
1. Open the .bashrc file with a text editor. The example below uses Vim:

2. Go to the end of the file.
3. Paste the export syntax at the end of the file.
export PATH="/Directory1:$PATH"
4. Save and exit.
5. Execute the script or reboot the system to make the changes live.
6. To verify the changes, run echo:

Editing the .bashrc file adds a directory to the PATH for the current user only. To add the directory to the PATH for all users, edit the .profile file instead.

Remove Directory from PATH in Linux
There isn’t a single command to remove a directory from the PATH, but there are several methods to achieve this.
Method 1: Exit the Terminal
Removing a directory from the PATH is straightforward when it has been added temporarily. Adding a directory in the terminal affects only the current session, and it is automatically removed once the session ends.
To remove a temporary directory from the PATH, simply exit the terminal or reboot the system.
Method 2: Edit Configuration Files
If the directory export string was added to the .bashrc or .profile file, you can remove it similarly. Open the file in a text editor, navigate to the end, and delete the directory entry.
Method 3: Apply the String Replacement Concept
To remove a directory from PATH, use string replacement:
export PATH=${PATH/'/Directory1'/}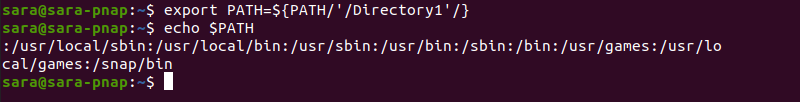
This command only removes the string for the current session.
Method 4: Use a One-Liner
Alternatively, you can use a combination of tr, grep, and paste to remove a directory from the PATH. For example:
export PATH="$( echo $PATH| tr : '\n' |grep -v Directory1 | paste -s -d: )"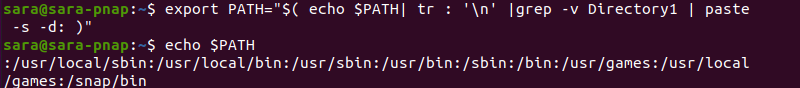
Conclusion
Having read this guide, you now understand how to add a directory to the PATH variable. Next, discover how to export Bash variables in Linux.



