Introduction
Python is a popular programming language widely used for automation and various types of scripting. Python 3, the latest version, offers performance improvements, new features, security patches, and enhanced compatibility with libraries and tools.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install Python 3 on Ubuntu 20.04 or Ubuntu 22.04.
Prerequisites:
- A system running Ubuntu 18.04 or Ubuntu 20.04.
- A user account with root privileges.
- Access to a terminal window/command line (Ctrl+Alt+T).
Check if Python Is Installed on Ubuntu
Before installing Python 3, verify if it is already installed on your system. Open a terminal and run the following command:
python3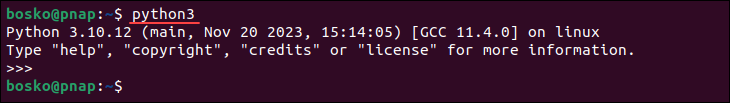
If the output displays the version number, Python 3 is already installed on your Ubuntu machine. You will also see additional information about copyright, license, etc. To exit the prompt, press Ctrl+D.
If the command returns an error stating “bash: python3: command not found,” Python is not installed.
Install Python on Ubuntu
There are several methods for installing Python on Ubuntu:
- Via APT: Install the latest version available in the default Ubuntu repository.
- From Source Code: Install the latest version from the official Python website.
- Via PPA: Install Python from the Deadsnakes PPA, a third-party repository designed for Ubuntu.
The following sections provide the steps for each installation method, allowing you to choose the one that best fits your needs.
Method 1: Install Python via APT
This process uses the apt package manager and the default Ubuntu repository to install Python. While this method is the easiest, it may not always provide the latest Python version. For the most up-to-date versions, you can check the official website or a third-party repository.
Follow these steps:
Step 1: Update the Package Repository
Update the package repository to ensure you get the latest available version. Run the following command:
sudo apt updateStep 2: Install Python
After updating the package repository information, run the following command to install Python:
sudo apt install python3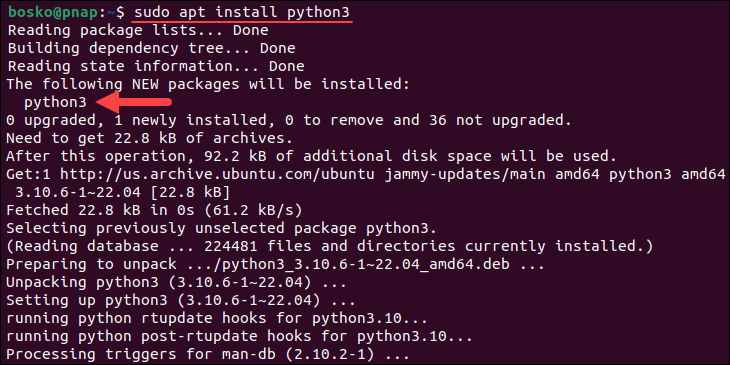
Wait until the installation finishes to start using Python.
Step 3: Verify Installation
Verify whether the installation was successful by checking the program version:
python3 --versionMethod 2: Install Python From Source Code
Use this method to download and compile the source code from the official developer. Although it is a bit more complex, it allows you to access the latest Python release.
Follow these steps:
Step 1: Update Local Repositories
Update the local package repositories:
sudo apt updateStep 2: Install Supporting Software
Compiling a package from source code requires additional software. Run the following command to install the necessary packages for Python:
sudo apt install build-essential zlib1g-dev libncurses5-dev libgdbm-dev libnss3-dev libssl-dev libreadline-dev libffi-dev wget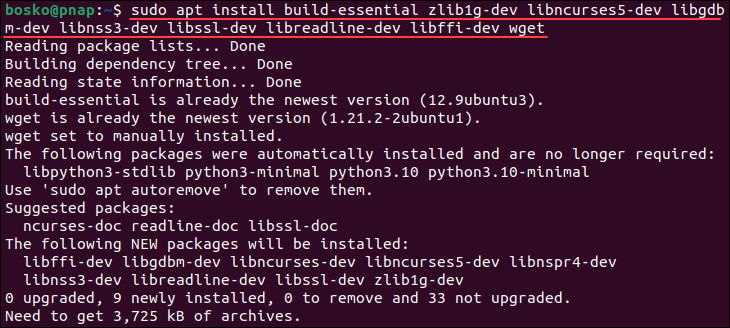
Step 3: Download the Latest Version of Python Source Code
1. Navigate to the /tmp directory with the cd command.
cd /tmpThe /tmp directory is often used for downloading source code because it is designated for temporary storage, making it easy to clean up downloaded files after installation.
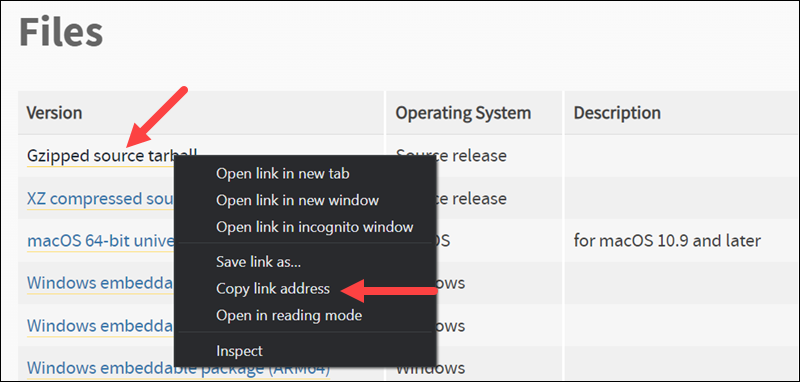
2. Navigate to the official Python source code webpage and select the version you want to install. Scroll down to the Files section and copy the link to the Gzipped source tarball:
3. Use the wget command and the link above to download the newest release of Python Source Code:
wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.12.1/Python-3.12.1.tgz
Step 4: Extract Compressed Files
In this step, extract the tgz file you downloaded. Run the command below:
tar -xf Python-3.12.1.tgzReplace the version numbers in the tgz file name with the one you have downloaded.
Step 5: Test System and Optimize Python
Before installing the software, it’s important to test the system and optimize Python.
The ./configure command evaluates and prepares Python for installation. Utilizing the --optimization option can enhance code execution speed by 10-20%.
Navigate to the directory where you extracted the .tgz file, and execute the following command:
./configure --enable-optimizations
The process takes some time to complete. Wait until it finishes before moving on to the next step.
Step 6: Install Python
After completing the optimization and testing, execute the following command to build the Python package:
sudo make installNote: If you already have Python 3 installed and want to create a second Python installation alongside it, run the following command:
sudo make altinstallAllow the process to complete.
Step 7: Verify Python Version
Check if the installation completed correctly by running:
python3 --versionThe command should display the version of the program you installed.
Note: If you’re new to Python and are still exploring IDEs or editors, check out our comprehensive overview of the best Python IDEs and code editors.
Method 3: Install Python via PPA
A Personal Package Archive (PPA) is a third-party repository in Ubuntu that provides a convenient method to access and install newer versions of programs not found in the standard Ubuntu repositories.
Follow these steps to install Python via a PPA:
Step 1: Update and Refresh Repository Lists
Open a terminal window and run the command below:
sudo apt updateStep 2: Install Supporting Software
Enhance your control over the package manager by installing the software-properties-common package. This software enables you to add PPA (Personal Package Archive) repositories. Execute the following command to install the necessary software:
sudo apt install software-properties-commonStep 3: Add Deadsnakes PPA
Deadsnakes is a PPA known for providing newer releases compared to the default Ubuntu repositories. Add the PPA by executing the following command:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppaAfter running the previous command, the system will prompt you to press Enter to continue. Once the process is completed, update the package lists again with the following command:
sudo apt updateStep 4: Install Python 3
The Deadsnakes PPA contains numerous Python versions in its database, enabling you to install older versions if needed. Specify the version in the package name to install that particular version.
For instance, use the following command to install Python 3.12:
sudo apt install python3.12
Confirm the installation with y and allow the process to complete.
Step 5: Verify Installation
Verify that Python is installed correctly by running:
python3 --versionThe output should state the program version you chose to install.
Conclusion
Now, you should have a functional installation of Python 3 on your Ubuntu system. Consider installing PIP for Python if you haven’t done so already.


